Cloud computing Concepts and Fundamentals
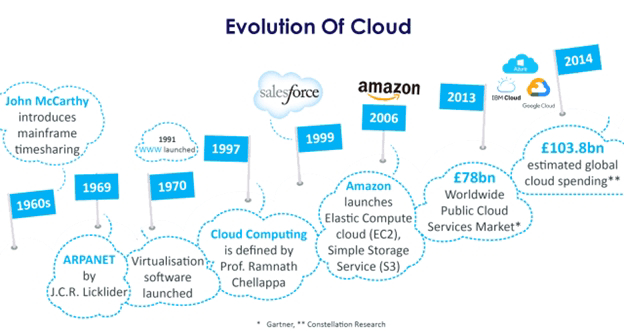
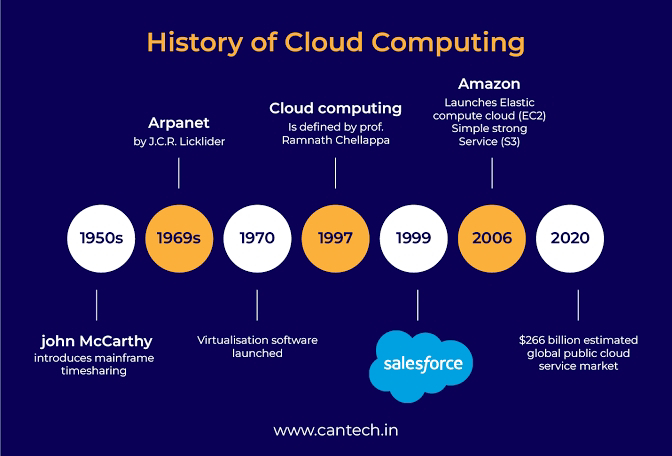
Past: Origins and Early Development
1960s–1990s:
Concepts: Introduced as time-sharing and virtual machines (mainframe era).
Grid Computing: Emerged to allow distributed computing power.
Client-server model: Gained popularity in the 1990s with the growth of the internet.
Early 2000s:
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Amazon Web Services (AWS) launched in 2006.
Software as a Service (SaaS): Salesforce (1999) pioneered cloud-hosted software delivery.
---
Present: Mainstream Adoption and Innovation
Key Models:
IaaS, PaaS, SaaS widely adopted.
Hybrid and Multi-cloud architectures in use.
Technologies:
Kubernetes & Containers: Enable scalable and portable applications.
Serverless computing: Developers run code without managing servers.
AI & ML in the cloud: Cloud platforms provide powerful AI tools and training infrastructure.
Security & Compliance:
Focus on Zero Trust models, encryption, and data governance.
Top Providers: AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform, IBM Cloud.
---
Future: Intelligent, Decentralized & Green
Edge Computing: Processing data closer to where it's generated (IoT, 5G, AR/VR).
Quantum Computing in the Cloud: Early access to quantum power via cloud platforms.
AI-Driven Cloud Management: Smart resource allocation, anomaly detection, auto-scaling.
Sustainability: Cloud providers investing in green data centers and carbon-neutral goals.
Decentralized Cloud (Web3): Distributed cloud storage and computation (e.g., IPFS, Filecoin).
×××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××
Cloud computing is a model that delivers computing resources, like servers, storage, and applications, over the internet, rather than requiring users to manage their own physical infrastructure. Key concepts include on-demand self-service, broad network access, resource pooling, rapid elasticity, and measured service. These characteristics enable users to access and utilize computing resources flexibly and efficiently. Here's a more detailed look at the concepts and foundations:
1. On-Demand Self-Service:
- Users can provision and access computing resources (servers, storage, etc.) without needing to interact with the IT staff of the service provider.
- This allows for rapid scaling of resources up or down as needed. 2. Broad Network Access:
- Cloud services are accessible from various devices (laptops, smartphones, etc.) over the internet, making it easy to work remotely or collaborate.
3. Resource Pooling:
- Cloud providers combine their physical and virtual resources to service multiple clients.
- This enables efficient resource utilization and economies of scale, saving users money.
4. Rapid Elasticity:
- Users can quickly scale resources up or down as needed, adapting to changing workloads.
- This eliminates the need for purchasing and maintaining physical infrastructure for peak workloads.
5. Measured Service:
- Cloud providers offer pay-per-use pricing models, allowing users to only pay for the services they actually use.
- This eliminates the need for upfront capital expenditure and provides cost transparency.
6. Core Components:
- Virtualization:Allows for the creation of virtual instances of resources, enabling efficient resource allocation and sharing.
- Data Centers:Physical facilities that house the servers, storage, and other infrastructure required to support cloud services.
- Networking:High-speed networking connections enable seamless communication between users and cloud resources.
7. Service Models:
- Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS):Provides access to computing infrastructure (servers, storage, networking).
- Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS):Offers a platform for developing and running applications, including tools and services for deployment.
- Software-as-a-Service (SaaS):Delivers software applications over the internet, eliminating the need for installation or local management.
8. Deployment Models:
- Public Cloud: Cloud services are offered by third-party providers to the general public.
- Private Cloud: Cloud resources are dedicated to a single organization and can be hosted on-premises or in a remote data center.
- Hybrid Cloud: Combines public and private clouds, allowing for flexible resource allocation and workload management.
9. Benefits of Cloud Computing:
- Cost savings: Reduced capital expenditure and operating costs through pay-per-use pricing.
- Scalability: Easily scale resources up or down as needed to meet changing demands.
- Flexibility: Access computing resources from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Accessibility: Users can access and utilize cloud services from various devices.
- Collaboration: Facilitates remote work and collaboration through secure sharing of resources.


Comments
Post a Comment